Do the terms RFID, BLE and NFC sound familiar. Surely in this age, one would have heard about them but with a constant lingering question in your mind – how do they work and what are their differences?
What is RFID and How does it work?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. Typically one can see these implemented in shopping malls as tags that are attached to items. These tags are used to sound of the beeper at the exits if the tags are not taken off indicating that it was not billed (tags are taken off once billed at the billing counter). These tags have information stored in them and are typically passive. They use the radio energy from the reader to reflect back the information stored. The disadvantage with methods like a bar-code is that it needs to be in the line of site to be read whereas RFID tags are embedded in the object and it can be read.

What is BLE and How does it work?
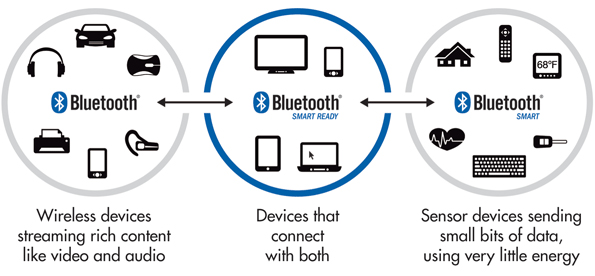
BLE is an acronym for Bluetooth Low Energy. Although it is called Bluetooth there is a difference between this and normal Bluetooth that we are using on our mobile devices.
In normal Bluetooth devices, the energy consumed is much higher than the of BLE devices. Regular Bluetooth operates in the frequency range 2400-2483.5 MHz through one of the designated 79 Bluetooth channels. Traditionally it is used for transferring a lot of data continuously for a longer duration in a short distance in M2M scenarios like transfer of files etc.
The BLE came in as part of Bluetooth 4.0 in 2011. It is typically used in short spurts of data transfer and the energy consumption is very low. A low-power device can last for 4 + years. It sends data for a couple of milliseconds while regular Bluetooth connects for 100s of milliseconds. The data transfer rates for BLE are also very high. BLE is not voice compatible.
The Bluetooth Smart Ready devices can connect with regular Bluetooth, Bluetooth Smart, or any Smart Ready device. A regular Bluetooth device is compatible with Bluetooth & Bluetooth Smart whereas a Bluetooth Smart device can only connect with Blue Tooth Smart device only. Regular Bluetooth has a limit of 100m while the BLE is greater than 100m.
What is NFC and How does it work?
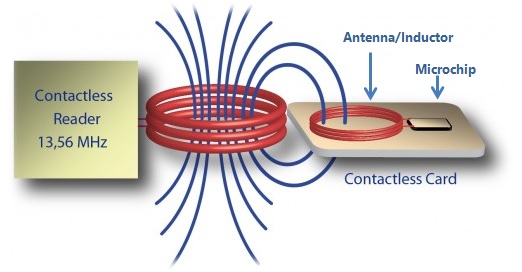
NFC stands for Near Field Communication, these devices too work on the Radio waves technology. It works by the principle of induction. It transmits at 13.56 megahertz with a max speed of 424 kilobits per second. Most tags are passive devices that contain an antenna and a microchip. The antenna is a coil and the NFC device picks power from the magnetic field. This power is used by the NFC tag to transmit information. Thus the magnetic field provides a communication medium as well as power.
It has 3 modes – peer-to-peer, read-write, and card emulation. It is used for small information exchange or to do a small action and now a days for card payments. One advantage with NFC is that it requires even lesser power than Bluetooth but this comes at a cost that the max range is very less to few inches while the Bluetooth goes 10m with the latest Bluetooth 5.0 going to 40m. Another big advantage with NFC is that there is no pairing needed and the connection is fast but the speed is low 424 kbps while it is 2Mbps in Bluetooth.
How are RFId, BLE and NFC different?